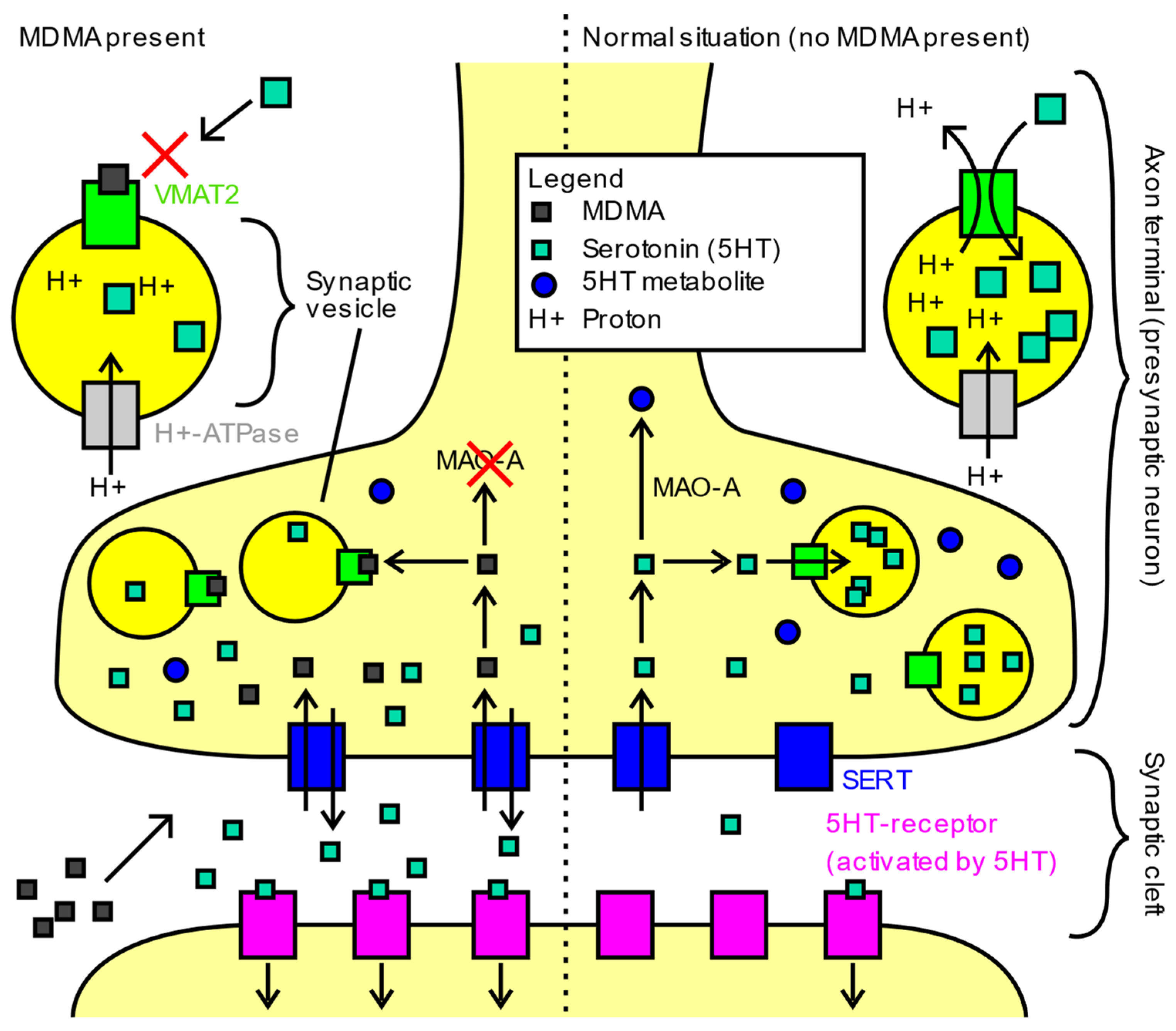
Clinically Relevant Pharmacological Strategies That Reverse MDMA-Induced Brain Hyperthermia Potentiated by Social Interaction | Neuropsychopharmacology
Clinically Relevant Pharmacological Strategies That Reverse MDMA-Induced Brain Hyperthermia Potentiated by Social Interaction | Neuropsychopharmacology
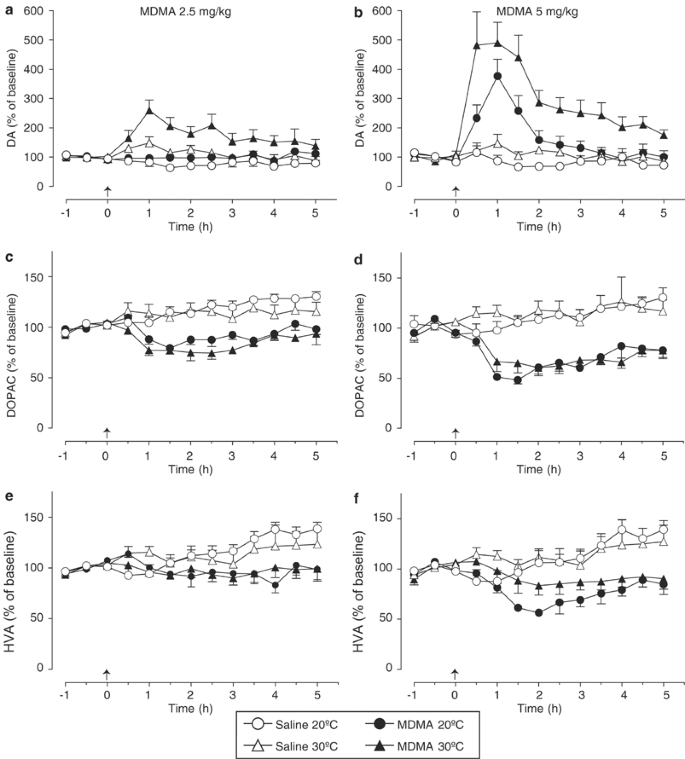
Elevation of Ambient Room Temperature has Differential Effects on MDMA-Induced 5-HT and Dopamine Release in Striatum and Nucleus Accumbens of Rats | Neuropsychopharmacology

Distinct neural mechanisms for the prosocial and rewarding properties of MDMA | Science Translational Medicine
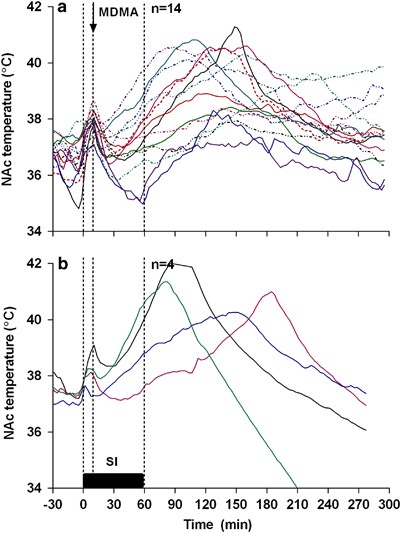
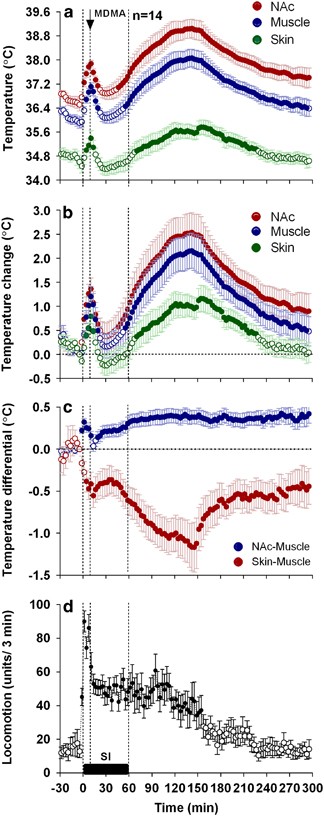
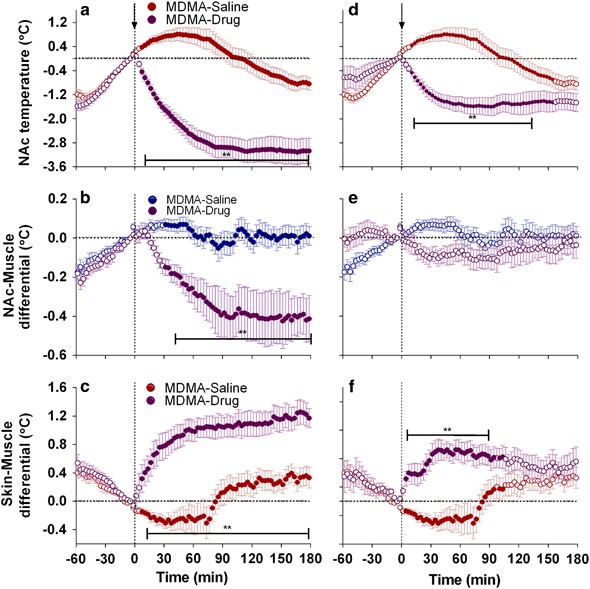
Clinically Relevant Pharmacological Strategies That Reverse MDMA-Induced Brain Hyperthermia Potentiated by Social Interaction | Neuropsychopharmacology

Critical Role of Peripheral Vasoconstriction in Fatal Brain Hyperthermia Induced by MDMA (Ecstasy) under Conditions That Mimic Human Drug Use | Journal of Neuroscience

Anorexia induced by activation of serotonin 5-HT4 receptors is mediated by increases in CART in the nucleus accumbens | PNAS

Persistent MDMA‐induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity in the striatum and substantia nigra of mice - Granado - 2008 - Journal of Neurochemistry - Wiley Online Library

SUPPLEMENTS GUIDE | 'Pre-rolling' and 'Post-Rolling' for MDMA to enhance the experience and reduce negative effects — Users News (UN)

Protective effect of nAc against mitochondrial dysfunction induced by... | Download Scientific Diagram

Critical Role of Peripheral Vasoconstriction in Fatal Brain Hyperthermia Induced by MDMA (Ecstasy) under Conditions That Mimic Human Drug Use | Journal of Neuroscience

Serotonergic Neurotoxic Metabolites of Ecstasy Identified in Rat Brain | Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics

Mice with Decreased Cerebral Dopamine Function following a Neurotoxic Dose of MDMA (3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine, “Ecstasy”) Exhibit Increased Ethanol Consumption and Preference | Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics
Non-Serotonergic Neurotoxicity by MDMA (Ecstasy) in Neurons Derived from Mouse P19 Embryonal Carcinoma Cells | PLOS ONE
Ecstasy induces reactive oxygen species, kidney water absorption and rhabdomyolysis in normal rats. Effect of N-acetylcysteine and Allopurinol in oxidative stress and muscle fiber damage | PLOS ONE
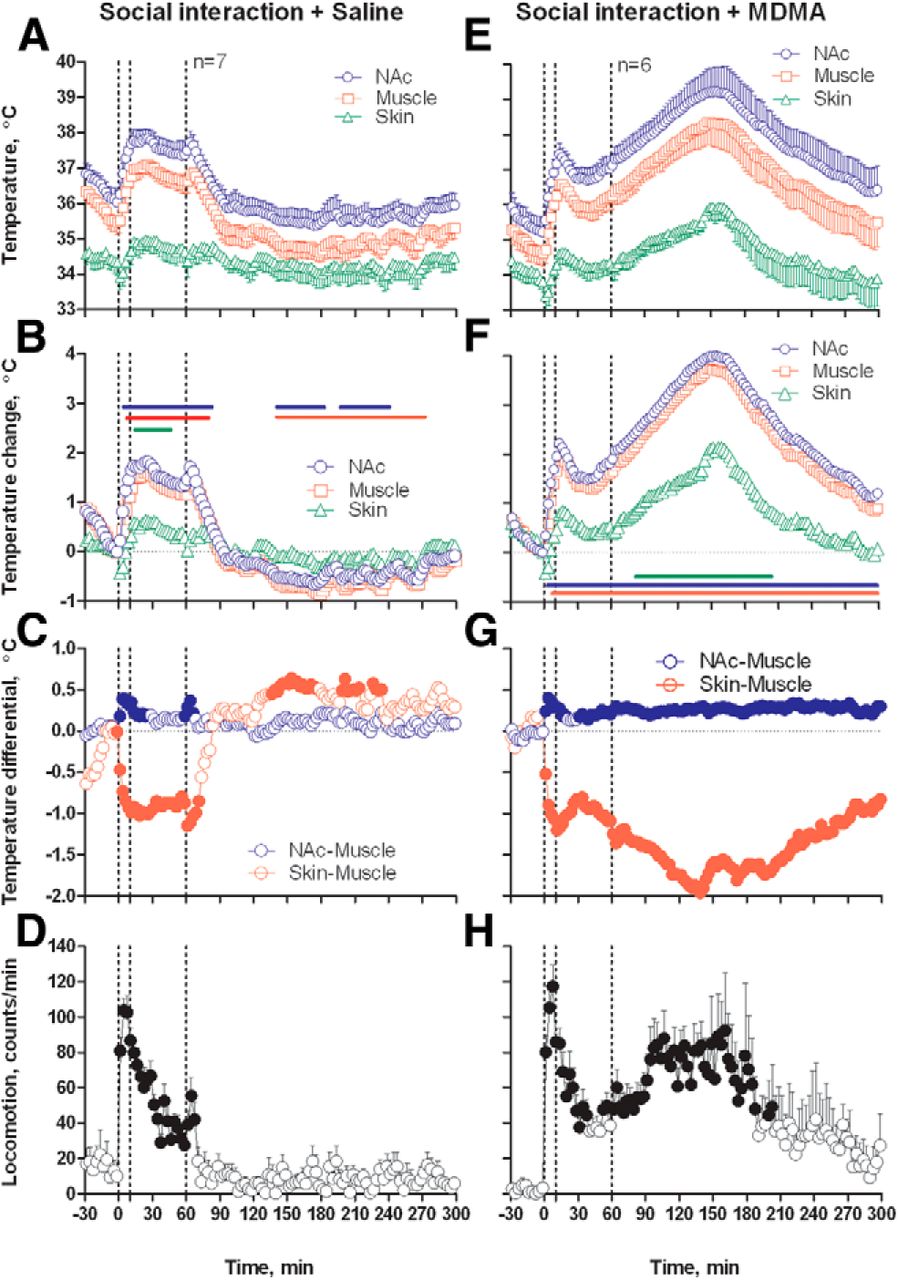
Critical Role of Peripheral Vasoconstriction in Fatal Brain Hyperthermia Induced by MDMA (Ecstasy) under Conditions That Mimic Human Drug Use | Journal of Neuroscience

Differential effects of intravenous R,S‐(±)‐3,4‐methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, Ecstasy) and its S(+)‐ and R(−)‐enantiomers on dopamine transmission and extracellular signal regulated kinase phosphorylation (pERK) in the rat nucleus accumbens ...

Differential effects of intravenous R,S‐(±)‐3,4‐methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, Ecstasy) and its S(+)‐ and R(−)‐enantiomers on dopamine transmission and extracellular signal regulated kinase phosphorylation (pERK) in the rat nucleus accumbens ...

Distinct neural mechanisms for the prosocial and rewarding properties of MDMA | Science Translational Medicine
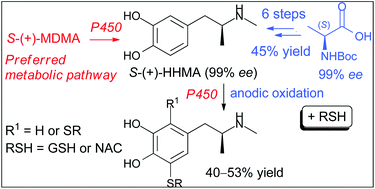
A convenient biomimetic synthesis of optically active putative neurotoxic metabolites of MDMA (“ecstasy”) from R-(−)- and S-(+)-N-methyl-α-methyldopamine precursors - Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry (RSC Publishing)

Dantrolene sodium fails to reverse robust brain hyperthermia induced by MDMA and methamphetamine in rats | SpringerLink
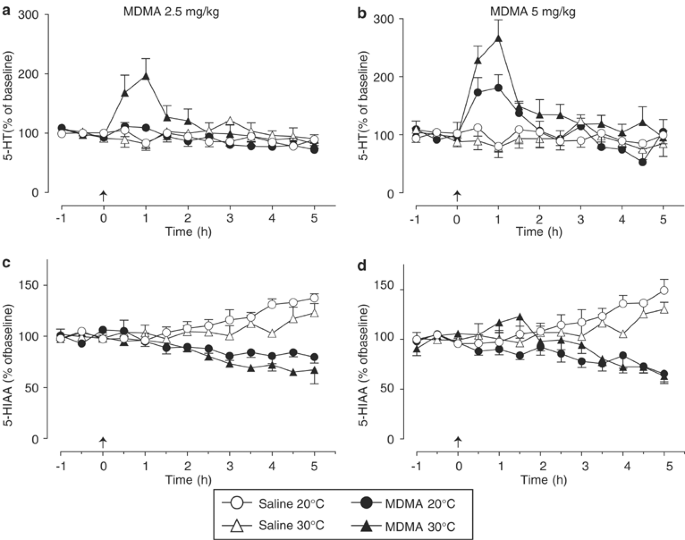
Elevation of Ambient Room Temperature has Differential Effects on MDMA-Induced 5-HT and Dopamine Release in Striatum and Nucleus Accumbens of Rats | Neuropsychopharmacology